DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP is network
protocol that is used for assigning various network parameter to a device or a
system. This greatly simplify administration of network, since there is no need
to assign manually network parameters for every devices.
DHCP is client-server
protocol. A client is a network device that is configure for using DHCP request
network parameter from DHCP server. DHCP server maintain a pool available IP
addresses and assign one to them to host. A DHCP server also provide some other
parameters, like that:
·
subnet mask
·
default gateway
·
domain name
·
DNS server
Cisco router can be configuring
as both DHCP clients and DHCP servers.
DHCP process explained:
DHCP client goes
through the four step:
2: The DHCP server
receive the DHCP Discover packet from client and respond with DHCP
Offer packet to the client, and offering IP address information.
3: If the client
receive the DHCP Offer packet from many DHCP server, the first DHCP Offer
packet is accept. The client respond by broadcasting a DHCP Request packets
to the server, and requesting the network parameters from the server that
respond first.
4: The DHCP server
approve lease with DHCP Acknowledgement packets. The packet
includes lease duration and other configuration.
NOTE
DHCP use a well-known UDP ports number 67 for DHCP server, and UDP port number
68 for client.
DNS (Domain Name System)
DNS is a network
protocol used for translating hostname into IP address. DNS is not requiring
for establishing a network connection, but it is more user friendly for users
than numeric addressing scheme. For example – you can access the Google by
typing 216.58.207.206, but it is more easier just by typing www.google.com!
For using DNS, you
have a DNS server configure to handle the translation process. A DNS has
special-purpose application installed. This application maintains table of
dynamic or static hostnames to IP addresses mapping. When user requests some
network resource using with hostname, (Like, by typing www.google.com in
a any browser), a DNS request is sent to DNS server asking for IP address of
the hostname. Then DNS server replies with IP address. The user browser can now
use that IP address to access www.google.com page.
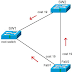
The below example
explain the concept of DNS:
Suppose that the DNS
Client want to commune with server named Server 1. Since DNS Client
does not know the IP address of Server 1, it sends DNS Request to DNS
Server, asking for Server 1 IP address. The DNS Server replies with IP
address of Server 1 (DNS Reply).
The below example shows
a sample DNS record, which taken from a DNS server:
Here you see that
host with the hostname APP1 is using the IP address of 10.0.0.3.
NOTE
DNS use well-known UDP port is 53.






2 Comments
Really it is very helpful..
ReplyDelete✔✔✔✔✔
ReplyDelete