EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) are an advanced distance vector routings protocols. This protocol is evolution earlier Cisco protocol called IGRP, which is now consider obsolete. EIGRP support classless routing & the VLSM, routes summarization, incremental update, load the balancing and many other useful features. It’s a Cisco proprietary protocol, therefore all the routers in the networks that is running EIGRP must be the Cisco routers.
Routers are running EIGRP
must be become neighbors before exchanging routings information. To the
dynamically discover neighbors. EIGRP routers use multicasts address of the
224.0.0.10. Each EIGRP router are stores routing and the topology information are
three tables:
· Neighbor table – store the information’s about
EIGRP
·
Topology table – store routings information
learned from neighboring's routers.
· Routing table – stores best Path.
Administrative
distance of the EIGRP is 90, which is less than the both administrative
distance of RIP and administrative distance of the OSPF, Therefore EIGRP
routes will preferred over these routes. EIGRP uses the Reliable Transport
Protocol (RTP) for the sending messages.
EIGRP calculates its
metric by the using bandwidth, delay, reliability & load. By default, only the
bandwidth and delay are used when the calculating metric, while reliability and
load are set to be zero.
EIGPR are uses the
concept of autonomous systems. An autonomous system is the set of EIGRP enabled
routers that they should become EIGRP neighbors. Each router inside an
autonomous system must be have the same autonomous systems number be configured,
otherwise routers will be not become neighbors.
EIGRP
EIGRP must be
establish neighbor are relationships with the other EIGRP neighboring routers
before exchanging routing information. To the establish neighbor relationship
routers are send hello for packets every couple of the seconds. Hello packets
are sent to multicast address of the 224.0.0.10.
The following fields
in hello packet must be identical in the order for routers to becomes neighbors:
·
ASN (Autonomous System Numbers)
·
Subnet Numbers
·
K values (Components of Metric)
Routers sends hello
packets every couple of seconds to the ensure that the neighbours relationships
is still actives. By default, routers are considering the neighbour to the down
after hold-down timer has expired. Hold-down timer is by default; three times hello
interval. On LAN network, the hold-down timer are 15 seconds.
Feasible and reported distance
Two terms that you
will be often encounter when are working with the EIGRP are feasible and the reported
distance. Let’s clarify are these terms:
·
Feasible distance (FD) –Metric of best
route to the reach network. That route will be listed in the routings tables.
·
Reported distance (RD) – Metric advertised by neighboring router for
the specific route. In other words, it’s the metric of route used by the neighboring router to reaches the networks.
To better the
understand concept, the consider are following examples.
EIGRP has been
configured on R1 and R2. The R2 are directly connected to subnet 10.0.1.0/24
and advertises that subnet into the EIGRP. Let’s say that R2’s metric to the
reach that subnet is 28160. When subnet advertised to the R1, R2 informs R1
that its metric to the reach 10.0.1.0/24 is 28160. From R1 perspective that
metrics considered to the reported distance for routes. R1
receives the update & adds metric to the neighbour to reported distance.
That metric is called are feasible distance and it’s stored in
R1’s routing table ((30720 in our cases)).
The feasible and
reported distance are displayed in the R1’s EIGRP topology tables:
R1#show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS
1/ID(192.168.0.1)
Code: P - Passive, A - Actives, U -
Updates, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - Reply status
P 10.0.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is
30720
via 192.168.0.2 (30720/28160), FastEthernet0/0Successor and feasible
successor
Another two the terms
that appears often in EIGRP world is successor and feasible
successor. Successor is route with the best metric to the reach a
destination. That routes are stored in routing table. A feasible successor is backup
path to the reach that same destination that can used immediately if successor
routes fails. These backup routes are stored in topology tables.
For routes to be
chosen as feasible successor, there are one condition must be met:
·
the neighbor advertised distance (AD) for route must be less than
successor feasible distances (FD).
The followings are
example explains in the concept of successor and the feasible successor.
R1 has two paths to
the reach subnet 10.0.0.0/24. The paths through R2 has best metrics (20) and
it’s stored in R1’s routings tables. The other’s routes, through R3 is a
feasible successors routes, because the feasibility conditions have been met
(R3 advertised distance of the 15 is less than R1 feasible distance of 20). R1
store that routes in the topology tables. This routes can immediately use if
the primary routes are fails.
EIGRP topology table
EIGRP topology table are
contains all the learned routes to a destination. The tables hold all the
routes received from neighbors, successors and feasible successors for every
routes and the interfaces on which the updates were received. The tables also
hold all the locally connected subnets included in the an EIGRP process.
Best routes from
topology table are the stored in routing tables. Feasible successors are only
stored in topology table & can used immediately if the primary route are
fails.
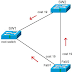
Consider the
following are network topology.
EIGRP are running on
all the three routers. Routers are R2 and R3 both connect to subnet 10.0.1.0/24
and advertise that subnet to the R1. R1 receives both update and the calculates
best route. The best path goes through R2. so R1 stores that the routes in
routing tables. Router R1 also calculates metric of route through R3. Let say
that the advertised distance of that routes are less than feasible distance of best
routes. The feasibility is condition met and router R1 store that the route in
the topology table as feasible successor routes. The route can use immediately
if primary route are fails.






1 Comments
Really very easy to understand thank for suck a superb tutorial....
ReplyDelete