What is IPv4 Address and its Role in the Network?
IPv4 or Internet Protocol version 4, address is a 32-bit number and separated by periods. It uniquely identifies a device interface in a network. IP is a part of the TCP/IP protocol suite, although IP is the set of rules for communication on the Internet. An IP address is needed to be assign on the devices, for example PCs, printer, servers, routers, switches, etc.
IPv4 Address Format
IPv4 address is show as a set of four block in decimal format, and each block is separated by dot. So, the term ‘dotted decimal format.’ every block is called an ‘octet’ because a block is composed 8 bits. below example shows the binary format of each octet:-
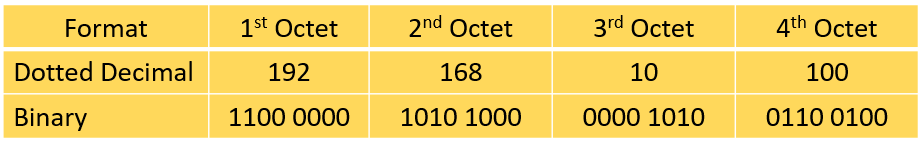
Numbers in an octet should be range from 0 to 255. thus, IPv4 address space will go from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. IPv4 address has two parts, first part is network part and the host part. A subnet mask will use to identify these parts.
Network Part
The network part of IPv4 address is on left-hand side. It specify the particular network to the IPv4 address belongs. The network part of the IPv4 address also identify that the IP address class of the IPv4 address.
For example, we have IPv4 address 192.168.10.100/24. /24 means that the first 24 bits, starting from left side is the network part of the IPv4 and 8 remaining bits of the 32 bits will be the host part.
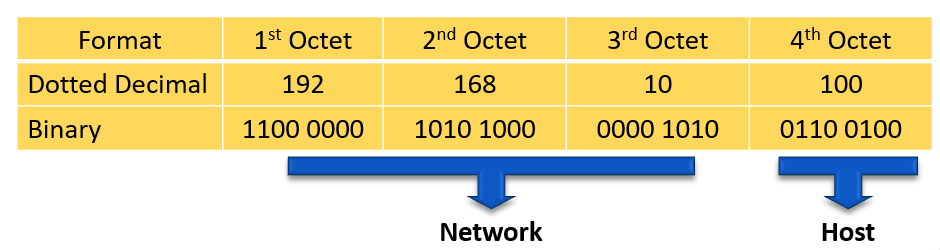
Host Part
The host part of the IPv4 is identify the device on your network. Hosts that have the same network part can communicate with each other without need for the traffic to be routed.
IPv4 Address Allocation
The IPv4 address can be assign to hosts or interfaces either manually or dynamically.
- Static – Static IP address is set manually on the device by the administrator. It is a best practice to assign static/manually IP addresses on network devices, for example, routers and switches, and on servers as well.
- Dynamic – Dynamic IP address is assign automatically to a device from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Dynamic IP addresses are best to be used on end devices, like PCs.
Types of IPv4 Addresses
There are two types of IP Addresses which are given below:-
- Public IP address – Is used to route Internet traffic. And for accessing internet and is given by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to customers.
- Private IP address – Is used in private network for internal traffic within Local area network Private addresses are not routed on the Internet.
Classes of IPv4 addresses
TCP/IP defines that the five classes of IP addresses: class A, B, C, D, and E. And each class has a valid range of addresses. The value of the first octet define the class. Addresses from the first three(A, B and C) classes can be used for host addresses. And the other two classes are use for other purposes – class D for multicasting and class E for researches purposes.
The classes created based on the network or host size. For example, for the small number of networks with a very large number of hosts so we will use class A. The Class C was created for many networks with least number of hosts.
Classes of IPv4 addresses are:
For IPv4 addresses from Class A, the first 8 bits specifies the network part, while the remaining 24 bits represent the host part. For Class B, the first 16 bits specifies the network part, while the remaining 16 bits specifies the host part. For Class C, the first 24 bits specifies the network part, while the remaining 8 bits specifies the host part.
Consider the following IP addresses:
- 10.50.120.6 – this is a Class A address and the first number "10" shows the network part, while the remainder of the address specify the host part "50.120.6". Means that, in order for devices to be on the same network, the first number of IP addresses has to be same for both device. In this case, a device with IP address of 10.47.8.3 is on the same network. The device with IP address 12.5.4.3 is not on same network, because the first number of the IP address is different
- 172.16.55.13 – This is a Class B address and the first two numbers "172.16" shows the network part, while the remaining part of the address shows the host part "55.13". A device with the IP address 172.16.254.3 is on same network.
The system of network address ranges represent here is generally bypassed today with the use of Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) addressing.
Some Special IP address are given below which are used for special purposes:
- 127.0.0.0/8 – loopback address
- 169.254.0.0/16 – link-local addresses (APIPA)
Subnet mask
An IP address is divided into two portions: network and host portions. For example, an IP class A address include of 8 bits specifying the network and the 24 bits specifying the host. because the default subnet mask for class A IP address is 8 bits long. ( written in dotted decimal notation 255.0.0.0). What does mean? Well, like IP address, a subnet mask also a 32 bits address. Computers use it to determine the network portion and the host portion of an address. The 1s in the subnet mask shows a network part and the 0s a host part.
Let’s say, we have an IP address of "10.0.0.1" with the default subnet mask of 8 bits "255.0.0.0".
Firstly, we need to convert IP address into binary:
IP address:- 10.0.0.1 = 00001010.00000000.00000000.00000001
Subnet mask:- 255.0.0.0 = 11111111.00000000.00000000.0000000
Computer use the AND operations to determine the network:
The computer can decide the size of the network. Only IP addresses that starts with 10 will be in the same network. So, the range of IP addresses in this network is 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255.
Slash Notation
Apart from the dotted decimal format, we also write the subnet mask in slash notation. It is a slash ‘/’ and follow by the subnet mask bits. To specifying the slash notation of the subnet mask, convert the dotted decimal format into binary, count the series of 1s, add a slash from the start.
Such that, we have the dotted decimal subnet mask of "255.0.0.0". In binary format, it is 11111111.00000000.00000000.0000000. And the number of 1s are 8, so the slash notation of 255.0.0.0/8.....





1 Comments
can I get the ppt slide of this topic..
ReplyDelete