VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary protocol used by Cisco switch to exchange VLAN information’s. With VTP, we can share VLAN information (such VLAN ID or VLAN name) with the other switch in the same VTP domain. A VTP domain is set of trunked switch with matching VTP setting (domain name, password and VTP version). All switches in the same VTP domain share VLAN information with the each other.
To understand true
value of VTP, consider example of network with 100 switch. Without VTP, if you
want to create VLAN on every switch, you would have to entered manually VLAN
configurations on every switch! And VTP enable you to create VLAN only on
single switch. And That switch spread information about the VLAN to every other
switch on the same VTP domain network and cause other switch to create it. if you
want to delete VLAN, you need to delete it on one switch, and change is
automatically spread to every other switch in the same VTP domain.
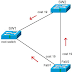
The below network
topology explain the concept of VTP:
On SW1, we create a
new VLAN. SW1 sends VTP update about new VLAN to SW2, which in turn sends it is
VTP update to SW3. These update will cause SW2 and SW3 to create the same VLAN
as SW1. You can see how this simplify the network administration – the engineer
had to log in and create the VLAN on first switch. And Other switch have
created the same VLAN’s automatically.
NOTE
VTP doesn’t advertise information about
which switches port are assigned to which VLAN.
VTP modes
NOTE
This topic is not available in the latest version of CCNA exam (200-301). If
you are learning for exam feel free to skip topic.
Every switch can use
one of the four different VTP mode:
·
VTP client mode – A switch using this mode can’t exchange
its VLAN configuration. Means that a VTP client switch cannot create or delete
VLAN. So, received VTP update are process and forward.
·
VTP server mode – A switch using this server mode
can create and delete VLAN. A VTP server switch will spread VLAN information to
it VTP client in same VTP mode. And this is default mode for Cisco switch.
·
VTP transparent mode – A switch
using this transparent mode does not share its VLAN information, but it forward
receives VTP advertisement. You can create and delete VLAN on a transparent
switch, but these change will not have sent to other switch.
·
VTP mode off – same like, VTP transparent
mode, with a difference that switch using this mode will not forwards have
received VTP update. This commands is support only in VTP V3.
As above mentioned,
all switch are configure as VTP server mode, by default. This is fine for
smaller networks without too many VLAs and VLAN change, since all VLAN
information can easily stored in every switch NVRAM. So, in larger network, it
is recommending to specifies couple of higher-quality switch to serve as VTP
server. All other switches in network should have to set up as VTP client mode.
Consider the below example:

We have network with
three switch. SW1 is configured as VTP server mode. After that the VLAN 5 is
created on SW1, this switch will notify to connected switch (SW2) about created
VLAN. SW2 will receive and update but, since it uses the VTP transparent mode,
it won’t create this VLAN in it configuration. So, it forwards the VTP update
to SW3. Since SW3 is configured as VTP client mode, it will process update and
create VLAN 5.
NOTE
This topic is not available in the latest version of CCNA exam (200-301). If you are learning for exam feel free to skip topic.




0 Comments