Computer commune with each other by using IP address, but we are using hostnames like www.google.com to access web server of Google where their website is host, With the use of DNS, we can able to access website with easily remembered names.
Imagine every time remembering IP address to access specific sites. That is not convenient way by typing only hostname on web browser like www.google.com instead of typing 142.250.181.46 IP address, which will simplifies process of accessing the sites.
What is a Domain Name System (DNS)?
DNS is decentralized and hierarchical name conventions system for computer or other resource that are connected to Internet or to Local Area Network (LAN). It use a hostname to identifies other computer systems. DNS solve issue of remembering all IP address by converting (resolving) them into hostname that website administrator can be customize. The primary purpose of DNS is resolve hostname to IP address. The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) or domain name of website is lot easier to remember compare to IP address of website.
Before DNS is being implement, the computer can use domain name by using host file. The host file contain the hostname and maps it to a specific IP. Whenever the computer want to visit website on the internet, it will check first on host file and map it to IP address of website. What if the hostname of website or IP address is not registered on host file? The computer will not be able connect to website.
Frequently updating host file is not convenient and efficient way as internet is continuously growing. To solve this issue, a DNS Server (Name Server) created. The DNS server are being root server for its domain and contain all DNS record for specific domain like TLD. Top-Level Domain (TLD) is domain that contain root (.) and ends name like .net, .com, or .org. On other hand, Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) contain a hostname, domain name, and TLD. While accessing www.google.com, “www” is the hostname, “google” is the domain name, and “.com” is TLD.
A hostnames represent network use to deliver a user to a specific address, while domain name is a site that user is accessing.
Domain Name System Operation
When computer is trying for accessing a website using with hostname – www.google.com, it will send DNS query or DNS lookup to DNS server and that will request IP address of website. Next, DNS server will respond with IP address (142.250.181.46) for www.google.com. When computer has IP address of website (www.google.com), it will request and established a connection to web server where website is hosted using IP address. The below example shows you the process of DNS.
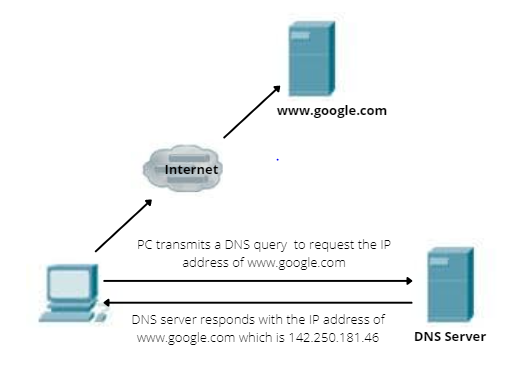
What if DNS doesn't have record for specific hostname. Then the DNS server will request and exchange information with the other DNS server located somewhere on Internet and will respond to customer with IP address of hostname. The DNS request are sent using UDP port 53. So, it can failover and use TCP...



1 Comments
I liked your explanation...
ReplyDeletegood and keep it up..