STP, Spanning Tree Protocol are enabled on all of vendors switches by the default. We have the different Spanning Tree modes both for the Cisco proprietary and for the open standard STP.
IEEE Open Standard Spanning Tree Modes
We have the followings
are IEEE STP standards, which are the used by all others vendors:
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) IEEE 802.1D – first &original
implementation of Spanning Tree Protocol standard. A single instance of
spanning tree is allowed in Local Area Network
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
(RSTP) IEEE 802.1w – improved version of the 802.1D STP. It’s faster for network to
the converge. However just like the 802.1D STP only a single instance of the
spanning tree is allowed in Local Area Network
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) IEEE 802.1s – allows us to the create multiple separate spanning-tree instances,
it’s enables us to the map and allocate
multiple VLANs to instances.
Cisco Spanning Tree Modes
We have the following
are Cisco proprietary STP standards which are the exclusively used by the Cisco
switches:
Per VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+) Protocol – Cisco-proprietary
enhancement to the IEEE 802.1D STP, it’s default spanning-tree version for the
Cisco switches. It’s enables us to the create one instance of the spanning-tree
per VLAN.
Rapid Per VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (RPVST+) Protocol – Cisco-proprietary
enhancement to IEEE 802.1w RSTP. Similar to the PVST+, it’s enables us to the
create a one the spanning-tree instance per VLAN as well. Network convergence
is also faster with the RPVST+.
Single Spanning Tree Vs Multiple Spanning Trees
With IEEE 802.1D STP
and 802.1w RSTP standards, all of VLANs will have the one spanning-tree
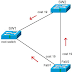
instance. Therefore, some will be taking suboptimal paths just like the example
topology below:
Since it’s a single
spanning-tree instance, there will single root bridge for all the VLANs in LAN.
this example, let say it SW1. All of the traffic will be forwarded to the SW1.
The Our multiple
spanning-tree modes, IEEE 802.1s MSTP, PVST+, & RPVST+, allow the us to
have be various spanning-tree instances. These instances are can take different
paths through network by the having different root bridges enabling’s load
balancing to the be possible. The traffic will take optimized paths for same
reason as well.
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) Example
With MSTP
spanning-tree mode, we have one the instance of the spanning tree for each
group of VLANs. Let say we have the following different departments in the our
office which are the assigned with the different VLANs:
·
(Sales Department) – VLAN 10
·
(Engineering Department) – VLAN 20
·
(Management Department) – VLAN 30
·
(Production Department )– VLAN 40
We can map Sales and
the Management departments to the SW1 as their root bridge. For Engineering and
Production departments, we can make the SW2 their root bridge. Now we have the two
instances of the spanning tree running.
For first instance,
the traffic for the VLAN 10 and VLAN 30 will forwarded to the SW1, and links to
the SW2 will be blocked. In second instance, the traffic for the VLAN 20 and
VLAN 40 will forwarded to the SW2 and will blocked on the SW1.
PVST+ and RPVST+ Example
PVST+ and RPVST+
Cisco Spanning-tree modes are the both Per VLAN spanning’s tree protocols. This
means that the every VLAN has are single instance of the spanning tree. We will
use this example of topology again:
For the example, we
want the traffic from Sales and the Management departments to the be forwarded
to their root bridge at the SW2 and blocked on SW1.
the traffic from the Engineering and
Production departments will forwarded to their root bridge at SW1, and SW2 will
be in the blocked state.
There will a total of
four spanning-tree instances running’s, as we have four VLANs in the network.
Assuming that we have the100 VLANs in our network, we will also have the 100
spanning-tree instances. It would be the consuming more resources as compared
to the grouping them like in the MSTP.
The spanning-tree
mode Command
We use spanning-tree
mode command to the show supported spanning-tree modes and to the select mode
to use for spanning tree configuration:
Switch(config)# spanning-tree mode ?
mst Multiple spanning tree mode
pvst Per-Vlan spanning tree mode
rapid-pvst Per-Vlan rapid spanning tree
mode






0 Comments